What You Need to Know About Soft Tissue Knee Injuries
By Zita ShamYour knees are complex joints that allow you to walk, run, and jump. These activities rely on a network of soft tissues – ligaments, tendons, muscles, and cartilage – susceptible to injury.
Understanding soft tissue knee injuries can help you identify the problem, seek proper treatment, and get back on your feet faster. We'll dive into those in this article and by the end, we will know exactly what to do (and not to do) after a knee soft tissue injury.
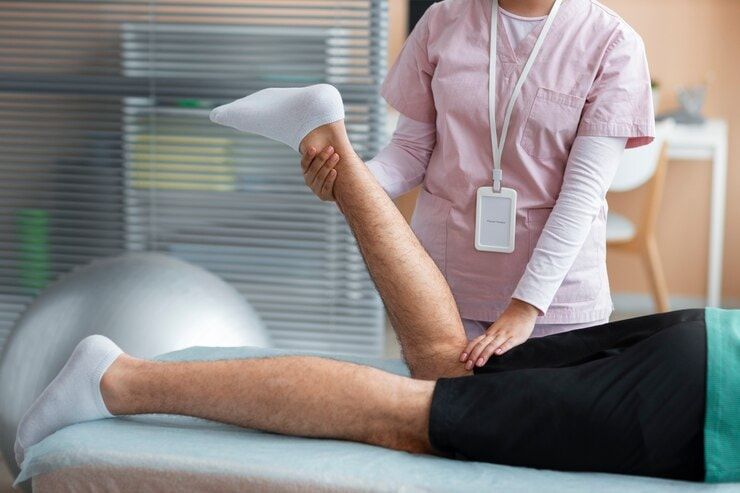

What Is Soft Tissue in the Knees?
The soft tissues in your knees are the various non-bony structures that work together to provide stability, flexibility, and cushioning. These tissues include the following:
- Ligaments: These are tough, fibrous bands of tissue that connect bones together.
- Tendons: These are also tough, fibrous bands of tissue, but they connect muscles to bones. This allows the muscles to move the knee joint.
- Menisci: These are two C-shaped pieces of cartilage that sit between the shinbone (tibia) and the thighbone (femur). They act as shock absorbers and help to distribute weight evenly across the knee joint.
- Muscles: Several muscles surround the knee joint and help to move it. The quadriceps muscles in the front of the thigh straighten the knee, while the hamstrings in the back of the thigh bend the knee.
Soft tissue injuries, particularly in the ligaments, are the most common types of knee injuries in Singapore. Let's further explore the common causes below.
How Does a Soft Tissue Injury Happen?
Soft tissue injuries can happen in various ways. A sudden twist or direct blow to the knee, often during sports or accidents, can cause a sprain (overstretched or torn ligament) or strain (pulled or torn muscle). Overuse and repetitive activities can also lead to soft tissue injuries, particularly in athletes.
There are four main ligaments that stabilise the knee joint. Each ligament has a specific role in keeping the knee joint stable.
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL): Controls rotation and forward movement of the shinbone.
- Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL): Prevents the shinbone from moving backward.
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL): Limits outward bending (inner side of the knee).
- Lateral collateral ligament (LCL): Limits inward bending (outer side of the knee).
Other soft tissue structures susceptible to injury include the meniscus (cartilage cushions between the shinbone and thighbone), patellar tendon (connects the kneecap to the shinbone), and quadriceps tendon (connects the quadriceps muscles in the thigh to the kneecap).
Types of Soft Tissue Knee Injuries
The knee joint relies on various soft tissues for stability and movement. Sadly, these are prone to injury. Some of the most common knee injuries involve damage to these soft tissues.
Posterior cruciate ligament tears are one type of soft tissue knee injury that can sideline you from activities. The PCL is a strong ligament located in the back of your knee. Its main job is to prevent your shinbone (tibia) from sliding backward relative to your thighbone (femur).
Below are other types of soft tissue knee injuries.
Ligament Sprains
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) on the inner knee and the ACL are particularly vulnerable to injuries.
Meniscus Tears
This C-shaped cartilage cushioned between your shinbone and thighbone can tear due to sudden twists or repetitive stress.
Tendonitis and Tendon Tears
The patellar tendon connecting the kneecap to the shinbone is a common target in this injury.
Other Knee Injuries
Other soft tissue injuries in the knees might include damage to the articular cartilage or the patellar ligament. In severe cases, a knee dislocation can happen, where the bones briefly pop out of the joint.
Recognising the Signs: Symptoms of Soft Tissue Knee Injury
Knee pain is the most common symptom of a soft tissue injury. Depending on the severity and location of the injury, you might experience:
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Stiffness
- Difficulty bending or straightening the knee
- Instability or a feeling of giving way
- Popping or snapping sound during the injury
Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly impact your healing process and minimise long-term complications.
Diagnosis: Getting to the Root of the Problem
A knee specialist, such as a sports medicine physician or orthopaedic surgeon, will typically diagnose a soft tissue knee injury through a physical examination and may order imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs to confirm the extent of the damage.
Treatment Options for Soft Tissue Knee Injuries
Treatment for soft tissue knee injuries depends on the severity of the injury and the affected structures. Below are some very common approaches.
First Aid (RICE)
In the immediate aftermath of a knee injury, employ the RICE principle (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation). Apply an ice pack wrapped in a damp towel to the injured area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Rest the affected knee and elevate it above your heart to reduce swelling.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
For mild injuries, your doctor might recommend anti-inflammatory medicines or over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain relief.
Physical Therapy
This involves regaining strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the injured knee. A physical therapist will design a personalised exercise programme specifically tailored to your injury and healing stage.
Surgery
In some cases, particularly for complete ligament tears or complex meniscal tears, surgery might be necessary to repair the damaged tissue and restore knee function.
Physiotherapy for Soft Tissue Knee Injuries: Getting You Back on Track
Soft tissue injuries can be more painful than you think. Knee pain physiotherapy in Singapore usually helps manage soreness and discomfort with the right treatment plan.
Physiotherapy providers for bone, muscle, joint, and tendon pain and injuries like Phoenix Rehab create a personalised treatment programme for your needs. This programme might include:
- Strengthening exercises for the quadriceps muscles, hamstrings, and calves to support the knee joint.
- Balance exercises to improve stability and proprioception (your body's awareness of its position in space).
- Stretching exercises to maintain flexibility and prevent stiffness.
- Manual therapy techniques like soft tissue massage to target specific areas of pain and inflammation.
How Long Does It Take to Recover?
The time it takes to recover from a soft tissue knee injury can vary from 3–12 weeks, depending on the severity of the injury and other factors. Acute knee injuries like strains and sprains may take 3–6 weeks to heal. Meanwhile, more severe and complex injuries involving ligament or meniscus tears may take 6–12 weeks. These may even require surgery and physical therapy for a full recovery.
What Not to Do
Refrain from engaging in higher-level activities following a knee injury. Avoid putting any weight on the injured knee until your doctor gives you the green light. This minimises stress on the joint and facilitates healing.
Additionally, resist the urge to apply heat to the area. While heat might feel comforting, it can actually worsen swelling. Cold therapy, on the other hand, is a better option. Applying ice packs wrapped in a towel can help reduce inflammation and pain.
Furthermore, you should avoid consuming alcohol, massaging the injured area, and smoking.
If there are still signs of pain or swelling after a few days, you should see your doctor in case you are dealing with an underlying condition, infection, or a serious injury.
Conclusion
Soft tissue knee injuries are common, but with proper diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation, you can return to enjoying your normal activities. Knowing the different types of soft tissue injuries, their causes, and symptoms will equip you with self-management techniques, especially for minor injuries or post-rehabilitation.
Browse other articles by category
Physiotherapy for Knee Pain Physiotherapy For Slipped Disc Physiotherapy for Neck Pain PHYSIOTHERAPY
PHYSIOTHERAPY
 Hand Therapy
Hand Therapy
 Alternative
Alternative
 Massage
Massage
 Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment
Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment
 Rehab
Rehab
 Physiotherapy For Lower Back Pain
Physiotherapy For Shoulder Pain
Orthopedic Doctors, Insurance & Healthcare
Physiotherapy For Upper Back Pain
Frozen Shoulder
Physiotherapy for Back Pain
Physiotherapy For Lower Back Pain
Physiotherapy For Shoulder Pain
Orthopedic Doctors, Insurance & Healthcare
Physiotherapy For Upper Back Pain
Frozen Shoulder
Physiotherapy for Back Pain
 Whatsapp us now
Whatsapp us now