Addressing Sharp Knee Pain: Identifying Causes and Seeking Relief
By Nigel ChuaSharp knee pain can be extremely limiting, impacting movement and overall quality of life. It can interfere with daily activities or result in further injury. Identifying the underlying causes of this pain is essential for proper treatment and relief.

Knee pain often occurs due to bone issues or irritation of the surrounding nerves. A sharp, stabbing sensation in one or both knees may also stem from a soft tissue injury or, in more serious cases, a severe fracture.
In this article, we’ll discuss the 15 most common causes of sharp knee pain, along with treatment options and relief methods to help restore comfort and mobility.
15 Most Prevalent Reasons for Sharp Knee Pain
The knee joint is made up of bones, ligaments, cartilage, muscles, and tendons that work together to support body weight, enable standing, and allow movement. Because it bears much of the body’s weight, the knee is highly susceptible to sharp pain and injury.
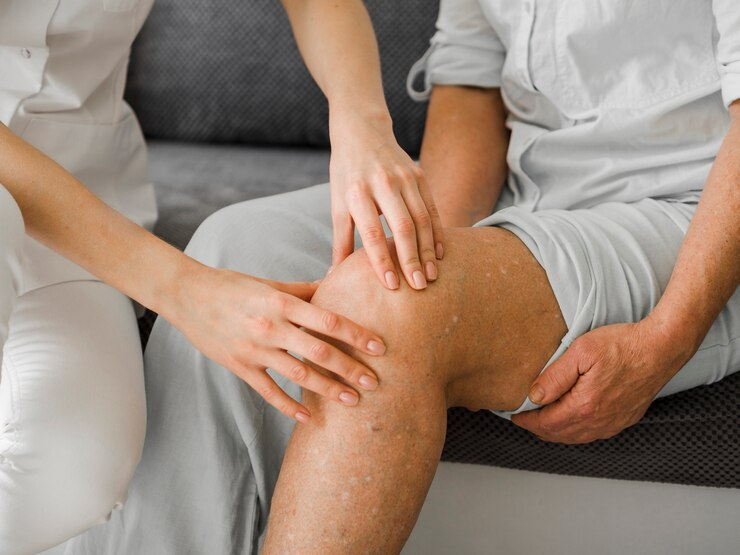
The good news is that many cases of sharp knee pain and related injuries may be managed with physiotherapy. Physiotherapy clinics in Singapore provide a wide range of treatments and exercises designed to support pain management and improve long-term knee health using a non-invasive approach.
It’s important to identify likely contributing factors to your knee issues early. If you’ve been experiencing sharp knee pain for some time, it may be linked to one of the following conditions.
1. Fractures
A broken bone can cause intense, sharp pain, especially when moving or putting weight on the knee. When resting, the pain may feel dull or achy. The fibula—the smaller bone in the lower leg is most often fractured, and a high fibula break can trigger sharp pain on the outer side of the knee. Fractures in the tibial plateau or femoral condyles typically cause sharp pain within the knee joint, while a patellar fracture, usually due to trauma or direct impact, is less common.
2. Knee Cartilage Tears
Tears in the knee cartilage, such as a meniscus tear, can lead to sharp pain, particularly during twisting movements. The cartilage covering the knee bones allows smooth, frictionless movement and absorbs impact during activities like running or jumping. When damaged, small cartilage fragments may break off and get trapped inside the joint, causing pain and discomfort.
3. Knee Bursitis
Knee bursitis occurs when the fluid-filled sacs near the joint (bursae) become inflamed. This often causes sharp pain, which worsens with kneeling or climbing stairs. The bursae normally cushion the bones and reduce friction, but irritation can make the pain flare up during activity and ease with rest.
4. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Joint conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis affect about 40% of Singapore’s population, with age being a key risk factor. Unlike osteoarthritis, which results from wear and tear, RA is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks healthy tissues. When RA affects the knees, it can cause anything from mild to severe pain, often accompanied by stiffness, swelling, warmth, or joint locking especially in cold weather or upon waking.
5. Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
This condition causes pain behind or around the kneecap, often during physical activities. It’s commonly linked to Runner’s Knee, Chondromalacia Patella, or Patella Alta. Pain usually appears when climbing stairs, running, or squatting but subsides during rest.
6. Soft Tissue Injuries
Damage to soft tissues like ligaments, tendons, or surrounding muscles can lead to sharp knee pain and instability. The pain often comes from cartilage damage or inflammation in the bursae. Physiotherapists can develop personalised treatment plans and rehabilitation programmes to help address soft tissue injuries and chronic knee pain effectively.
7. Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Tears
An MCL tear causes sharp pain on the inner side of the knee. These injuries vary in severity, ranging from partial tears affecting some fibers to complete tears that fully separate the ligament.
8. Meniscus Tear
Meniscus tears cause sharp pain and may produce a clicking sound during movement. Pain is typically felt along the joint line, either on the inner or outer side, and worsens during squatting or twisting. Swelling and intermittent pain are also common.
9. Runner’s Knee
Runner’s knee results from overuse, improper movement, or structural imbalances. Symptoms include sharp pain and sensations of rubbing or grinding near the kneecap. Some experience sudden sharp pain, while others feel a persistent dull ache.
10. Dislocated Kneecap
A dislocated kneecap causes sharp pain at the front of the knee and often requires medical attention to realign the patella. Standing or applying pressure can worsen the pain, and tenderness usually remains even after initial discomfort subsides.
11. Nerve Irritation
When nerves around the knee are irritated, it can trigger sharp, shooting, or burning pain. This may result from issues in the lumbar spine, pelvis, or localised nerve damage sometimes following surgery or due to arthritis.
12. Loose Bodies
Loose fragments of bone or cartilage inside the knee can disrupt movement and cause symptoms like sharp pain, locking, catching, or swelling. These pieces typically result from injury or joint degeneration.
13. Septic Arthritis
This occurs when bacteria, viruses, or fungi infect the joint, leading to sharp pain, fever, swelling, redness, and warmth. Immediate medical care is crucial to prevent long-term joint damage.
14. Knee Gout
Gout in one or both knees causes sudden, intense pain, swelling, and redness during flare-ups. The pain typically worsens within the first 24 hours and may last up to two weeks. Because it can severely affect mobility, early treatment is recommended.
15. Repetitive Stress
Overuse injuries develop from repetitive strain that exceeds tissue capacity, commonly affecting athletes or those with physically demanding jobs. These injuries can impact muscles, tendons, cartilage, or bone, resulting in sharp or aching pain.
Understanding the Triggers of Sharp Knee Pain
Sharp or stabbing pain in the knee can be distressing, especially when it interferes with normal movement or daily activities. The discomfort may stem from sudden knee injuries or gradual wear and tear in the knee joint. Below are some common causes that may explain why you experience sharp knee pain or pain in the knee when twisting or bending.
Injury-Related Causes
- Torn Ligament or Cartilage: Damage to the ligaments or a cartilage tear (such as a meniscus injury) often results from a knee injury or sudden twisting motion. This can cause sharp pains or a stabbing pain that worsens when bearing weight.
- Fracture: A knee fracture or joint fracture involving the knee bone or thigh bone can lead to severe knee pain, swelling, and restricted movement. More severe fractures or broken bones may require immediate medical care.
- Bursitis: When the knee bursa becomes inflamed, typically an inflamed bursa near the kneecap, it can cause acute pain, tenderness, and swelling.
- Patellar Tendinitis: Also called patellar tendinopathy, this affects the tendon connecting the knee cap to the shin bone. It may feel like a sharp stabbing pain below the kneecap, especially after physical activity.
- Patellar Subluxation: A twisted knee or sudden shift that pushes the kneecap slightly out of its normal alignment can trigger sharp knee pain twisting and a sharp, stabbing sensation.
Medical Conditions That May Cause Knee Pain
- Arthritis: Both knee arthritis and osteoarthritis can cause a mix of dull aches and intermittent sharp pain. The affected joint may also feel stiff or swollen.
- Gout: Caused by uric acid crystal deposits in the joint, gout can lead to intense and sudden attacks of sharp pain and swelling in the knee.
- Nerve Irritation: Either some nerve irritation near the spinal cord or brain and spinal cord pathway can cause burning sensation, shooting pain, or referred pain to the knee.
- Loose Body or Bone Fragment Floating: Small fragments of bone or cartilage may move freely within the knee joint, causing a catching or locking feeling. This can limit movement until the loose body is removed from the knee structures.
- Tight Muscle or Ligament Sprain: A ligament sprain or tight muscle around the knee may contribute to discomfort or hinder movement.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Consult a doctor or physiotherapist if your knee pain persists or worsens despite rest. It is especially important to seek medical care if you experience:
- Severe knee pain following a fall or injury
- Obvious swelling, deformity, or if the knee cannot bear weight
- A visible bone fragment or suspected fracture
- Sudden swelling, redness, or warmth around the knee joint
- A burning sensation or stabbing pain that spreads down the leg
- Signs of infection such as fever or chills
Early assessment can help identify underlying knee problems such as joint tears, cartilage tear, or severe fractures. Management may include rest, knee braces, anti inflammatory medications, or physical therapy under professional supervision which may help support recovery and prevent the risk of recurring knee pain.
Information to Share with Your Doctor
When consulting a healthcare provider, providing detailed information helps with accurate assessment and treatment. Be ready to share:
- The exact spot and nature of your knee pain (sharp, stabbing, or shooting pain)
- When the discomfort began and if it worsens with certain activities
- If you experienced a twisted knee, fall, or knee injury before the pain started
- Whether certain motions or positions cause relief or make the pain worse
- Any swollen knee, bruising, or popping sensation
- If you’ve felt a pain like a sharp knife/stabbing pain or heard a snap at the moment of injury
After diagnosis, your doctor or physiotherapist may recommend physical therapy until normal knee movement returns, as it may help improve muscle strength and promote ease of movement. Early treatment and proper rehabilitation may help reduce the risk of long-term knee problems and prevent knee pain from becoming chronic.
Sharp Knee Pain Treatments and Relief
When dealing with sharp knee pain, it’s recommended to seek treatment early rather than relying on surgery or injections. Common approaches include:
- RICE Method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation may help reduce inflammation, ease discomfort, and promote healing.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medication: Over-the-counter or prescription drugs may help relieve pain and swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Personalised exercises and stretches help to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, restore movement, and may help support recovery without relying solely on surgery or injections.
Summary
Sharp knee pain can disrupt daily life, but identifying the cause and seeking proper treatment may help bring relief and mobility. With the right therapies and guidance, it’s possible to improve comfort and function. If pain persists, consult a physiotherapist early for personalised guidance and early intervention.
Browse other articles by category
Physiotherapy for Knee Pain Physiotherapy For Slipped Disc Physiotherapy for Neck Pain PHYSIOTHERAPY
PHYSIOTHERAPY
 Hand Therapy
Hand Therapy
 Alternative
Alternative
 Massage
Massage
 Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment
Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment
 Rehab
Rehab
 Physiotherapy For Lower Back Pain
Physiotherapy For Shoulder Pain
Orthopedic Doctors, Insurance & Healthcare
Physiotherapy For Upper Back Pain
Frozen Shoulder
Physiotherapy for Back Pain
Physiotherapy For Lower Back Pain
Physiotherapy For Shoulder Pain
Orthopedic Doctors, Insurance & Healthcare
Physiotherapy For Upper Back Pain
Frozen Shoulder
Physiotherapy for Back Pain
 Whatsapp us now
Whatsapp us now