Edema Swelling Therapy
By Nigel ChuaEdema and swelling is our body's natural way of healing an injury. When a part gets injured, the body sends its natural repair workers through fluids to fix it. These fluids usually accumulate in the injured location/part.
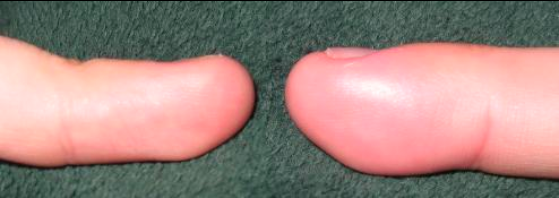
Unfortunately, there are two common problems that come with these repair workers.
- Firstly, these repair workers are good at repairing stuff, including injuries. However, they tend to cause stiffness due to their repair works.
- Secondly, together with these workers, come substances that cause pain and ongoing swelling.
If you see a doctor, be it a general practitioner or specialist doctor, they may prescribe you anti-diuretics and anti-inflammatory medication to bring down the swelling and pain. Too much fluid can increase pressure and cause damage to the organs and tissues.
This in turn can cause
- delays to healing
- additional and prolonged pain experiences
- increased stiffness.
This will impair and compromise clinical and functional outcomes.
That's why our senior physiotherapists and hand therapists in our physio clinics will quickly work on edema and swelling therapy management. This will take precedence first, followed by pain management, and then any forms of active movement or motion therapy.
Yes, it's important that we facilitate the healing and movement process, but we need to decrease the amount of swelling first, because swelling and edema will get in the way of healing.
EDEMA SWELLING PHYSIOTHERAPY
In our physiotherapy clinics, Phoenix Rehab uses a number of edema and swelling management techniques and approaches. Some of these include:
- Rest - it's very important to have the right balance between exercising/moving the injured site and rest. Too little rest, and the injury will not heal well; too much rest will result in a lot of stiffness and decreased range of motion. Our senior physiotherapists and hand therapist will assess and determine your body's balance to ensure best mobility, strength and functional results in managing edema and swelling.
- Elevation of the injured part in a position higher than the heart (not too high, as that can be uncomfortable and may lead to compromised blood supply to the elevated limb). This allows gravity to help with the removal of the excess fluids in the injured area. You can use pillows, or you may want to consider a pillow foam leg elevator.
- Compression using fingers (as in retrograde massage) or using compression garments will help with venous return to manage edema and swelling.
- Icing/cold therapy is used when there is medical clearance and no safety contraindications to using ice (such as open wounds or adverse reaction to cold temperatures). Cold therapy will help to decrease muscle spasms, as well as encourage the contraction of the affected area.
- Ultrasound therapy may help to accelerate soft tissue healing, which decreases edema and swelling. This can be used to complement edema therapy.
- Active muscle pumping and motion acts as a pump that accelerates the entry and exit of fluids entering and leaving the injured area. Moving the joints will also help maintain active range of motion for the unaffected joints.
- Retrograde massage and deep tissue release therapy may be helpful to improve fluid movement and return, to prevent "pocketing" of fluids.
If you have persistent edema and swelling in any areas of your body,please see a doctor or book a session with us at Phoenix Rehab, so we can assess and rule out any more serious issues.
Browse other articles by category
Physiotherapy for Knee Pain Physiotherapy For Slipped Disc Physiotherapy for Neck Pain PHYSIOTHERAPY
PHYSIOTHERAPY
 Hand Therapy
Hand Therapy
 Alternative
Alternative
 Massage
Massage
 Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment
Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment
 Rehab
Rehab
 Physiotherapy For Lower Back Pain
Physiotherapy For Shoulder Pain
Orthopedic Doctors, Insurance & Healthcare
Physiotherapy For Upper Back Pain
Frozen Shoulder
Physiotherapy for Back Pain
Physiotherapy For Lower Back Pain
Physiotherapy For Shoulder Pain
Orthopedic Doctors, Insurance & Healthcare
Physiotherapy For Upper Back Pain
Frozen Shoulder
Physiotherapy for Back Pain
 Whatsapp us now
Whatsapp us now