Brachialis strain pain physiotherapy
By Nigel ChuaA brachialis strain or brachialis tear is a common injury that occurs when you overstretch or overwork the brachial muscle in the upper extremity.
It is typically characterized by:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Muscle tightness
- Loss of strength in the arm or elbow
If you often feel pain shooting up your hand during certain movements, such as turning a knob, holding a cup of coffee, or using a screwdriver, it might be due to a brachialis tear.
Brachialis sprains are usually seen in people who frequently participate in physical activities like rope climbing or perform workouts involving a lot of pull ups and curls. Hyperextension or sudden forceful contraction of the elbow joint can also trigger brachialis pain.
The condition is not serious and most of the time, it can be easily treated at home. However, if the pain and swelling persists, you must consult a physician or see our physiotherapists or hand therapists as soon as you can.
In this article we discuss the symptoms and causes of brachialis strain. We also explore its treatment options and how physiotherapy can provide lasting relief from brachialis pain.
WHAT IS THE BRACHIALIS MUSCLE AND WHAT DOES IT DO?
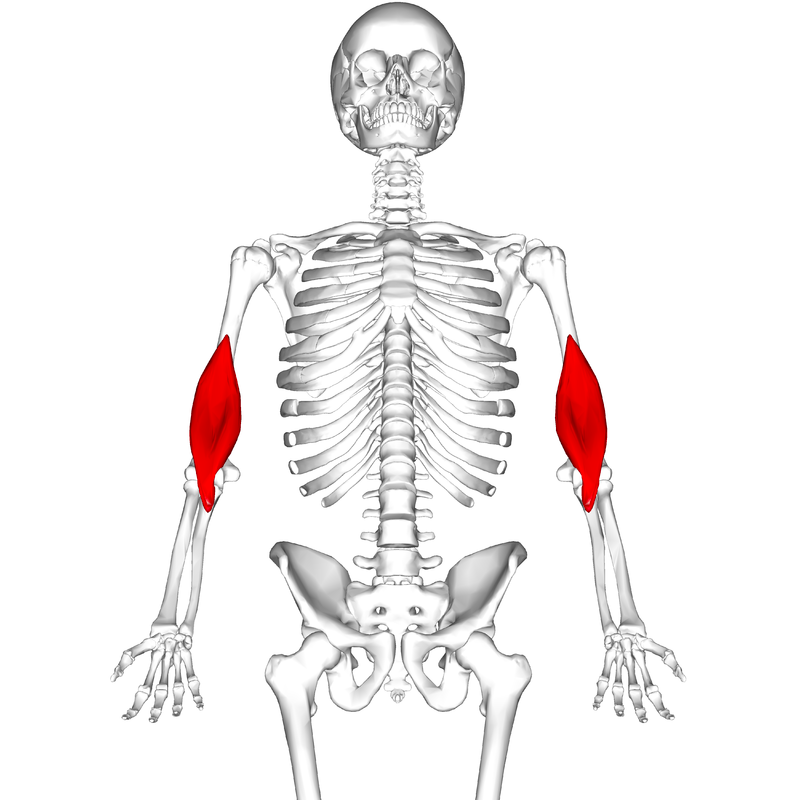
The brachialis muscle is not a commonly known or discussed topic, which is why many people have trouble identifying pain associated with its overuse until it becomes too severe.
To understand the symptoms of brachial tear and what can cause the muscle to become strained, you need to know the location and function of the brachialis muscle.
Understanding the anatomy of the brachialis can help you fully recover after an injury.
The brachialis is the main flexor of your elbow joint. It is situated about a centimeter away from the coronoid and attaches the ulna to the front of the humerus. It is covered by biceps brachii and has two main nerves running close to it – the brachial artery and the recurrent radial artery.
Simply put, the brachialis muscle allows you to bend your elbow. Every time you lift something that involves your elbow, such as:
- doing a push up
- cutting a slice of meat
- throwing a basketball
your brachialis muscle is activated.
A sudden force or extensive use of your arm or wrists may overload the brachialis muscle. This can culminate in mild to acute inflammation and in severe cases, lead to muscle tear.
When this happens, you are likely to feel pain in the upper arm. At times, the pain may be accompanied by swelling, numbness or weakness in the forearm or fingers.
Delaying treatment and continuing to use a torn brachialis can increase your chances of developing tendinitis. If the muscle tears away from the elbow joint, it can lead to an avulsion fracture which can greatly limit your range of motion.
At an even higher stage, nerve damage may occur and show as permanent deformity of the hand.
WHAT CAUSES BRACHIALIS STRAIN?
While it can be hard to identify the exact cause of brachial pain, muscle strain is usually the leading cause of this condition.
There are many different factors that can result in the brachial muscle being strained. For example:
- Weightlifting
- Prolonged bending of the elbow at an odd angle
- Sports injuries
- Working with heavy tools
- Recent illness
- Trauma
- Surgery
- Immunization or any other medicinal shots in the forearm muscle
These can all contribute to a brachialis strain as they make the muscle tender, and eventually, painful.
A direct injury can also be the causative force behind brachialis tears. For example, falling on your arms or hitting your elbow against a hard object can cause this muscle to become damaged due to the sudden and forceful impact.
SYMPTOMS OF BRACHIALIS STRAIN

Extreme tightness of the muscles in your forearm is the most common symptom associated with brachialis strain.
Generally, the pain intensifies when you perform certain actions that activate this muscle, e.g. shaking hands with someone, opening a door, or turning a gear stick with the affected arm.
The pain is normally felt in the forearm, but depending on the severity of the strain, the discomfort may extend to the back of your hand, especially the thumb and the index finger.
Other ways to identify a brachial strain include:
- Weakness in the arm muscles
- Piercing, sharp or radiating pain along the arm
- Pain starting in the shoulder or near the crease of elbow
- Soreness over the front of the elbow
- Difficulty in bending or completely straightening the elbow
- The elbow is sensitive to touch
- There is a popping sound when you flex your arm
- You feel something in your elbow joint move or ‘crack’ every time it is moved
OTHER CONDITIONS SIMILAR TO BRACHIALIS STRAIN
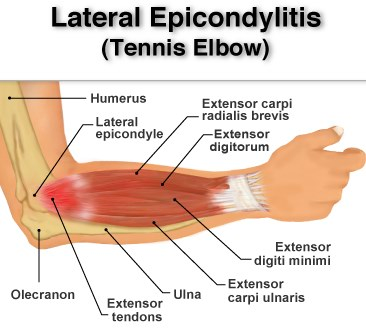
Brachialis strain and the accompanying pain is widely confused with lateral epicondylitis (commonly known as Tennis Elbow).
Although the symptoms of brachialis strain tend to mimic those of Tennis Elbow, the two conditions are totally different and require different treatment.
Due to the location of the pain, brachialis muscle injury can also be confused with medial epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow).
Therefore, when describing your symptoms to a physician, try to be as precise as you can.
You doctor may perform additional scans to avoid misdiagnosis and pinpoint where the injury has occurred.
WHO IS AT RISK OF EXPERIENCING BRACHIALIS STRAIN?
- People who frequently partake in recreational activities like rock climbing are at high risk of experiencing a brachialis strain.
- People whose jobs involve a lot of manual labor (e.g. lifting heavy objects like books or furniture) are also at high risk of this injury.
- Construction workers who wield a chainsaw on a daily basis are likely to develop a brachialis tear.
- Athletes are more susceptible to brachialis muscle damage, especially if they play tennis, bowling, or rowing.
- Parents or daycare workers who frequently lift and hold children with their elbows bent improperly are prone to straining their brachialis muscle.
- Playing musical instruments like the violin or guitar for prolonged hours can increase your chances of suffering from brachialis pain.
- Overdoing fitness exercises like pull ups, arm curls, chin ups, or anything involving excessive elbow flexion can rupture the brachialis muscle at the joint.
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR BRACHIALIS STRAIN
Brachialis strain is usually treated with massage and physical therapy, especially if the pain is mild to moderate. However, aggravated conditions may require supplemental medical treatments, such as cortisone injections. In extreme scenarios where response to conservative treatment methods is refractory, surgery may be required eventually.
People who experience a brachialis strain and seek professional help on time are usually able to recover successfully without the need for surgical methods.
If you are diagnosed with brachialis strain, your doctor may recommend traditional methods for pain control. Some of these are discussed briefly below.
PAIN RELIEF TIPS
As with most overexertion injuries, the first step to treating brachialis strain usually involves the RICE technique. RICE stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. It can be effective if you:
- Limit the use of your affected arm and elbow as much as possible, for about 72 hours after the injury or onset of pain (Rest).
- Apply an ice pack to the aching muscle for around 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours (Ice).
- Loosely wrap the elbow joint and forearm with a medical bandage or a soft flannel (Compression). This helps reduce swelling.
- Keep the affected arm at an elevated level, for instance, while sitting or lying down (Elevation).
HOW PHYSIOTHERAPY CAN HELP PEOPLE WITH BRACHIALIS STRAIN
While you can implement the RICE method for pain control at home, it is highly recommended that you follow up with a physical therapist for lasting relief from pain.
Our expert physiotherapists in Phoenix Rehab have helped several individuals with brachialis strain get rid of the ache, and can develop a personalized treatment plan for you too.
Broadly speaking, we use special stretching and strengthening exercises to alleviate pain and help the strained muscles heal naturally. We will start the session by completing an in-depth assessment and differential diagnosis, to pinpoint exactly what the painful condition is, as well as identifying the activities, actions and habits that aggravate it.
If the pain is so severe that the patient has difficulty bending the elbow or rotating their wrist, we begin with basic moves. Once the pain subsides, we use isometrics and strength training to gradually restore proper function of the affected parts.
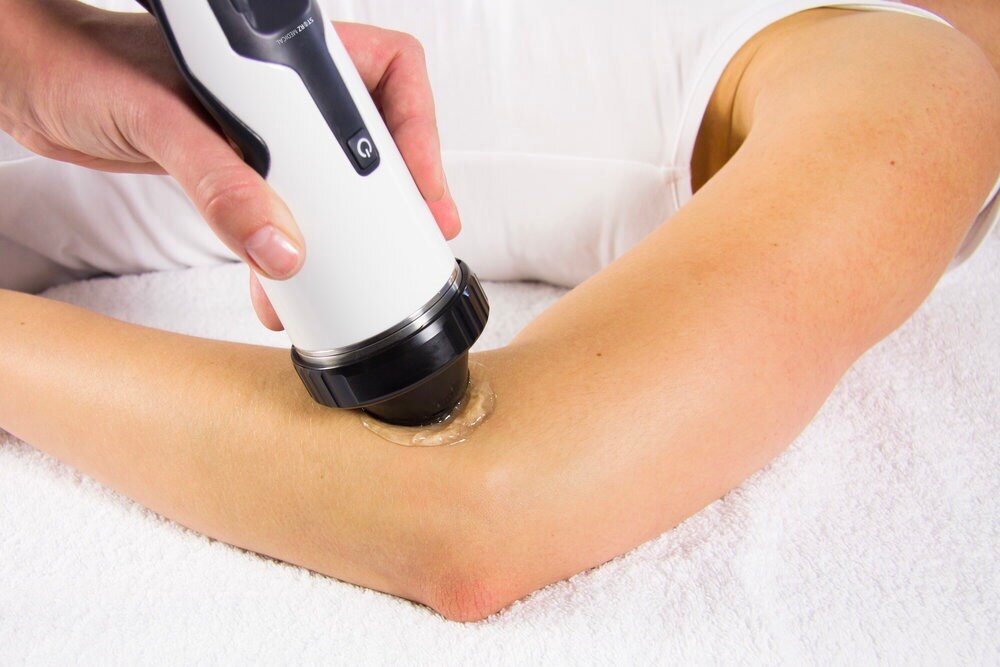
Since we follow a holistic approach to treating all muscle and joint injuries, your treatment for brachialis strain might also involve:
- Manual Therapy and Massage: The brachialis muscle has various trigger points that can help control pain if activated gently via massage. Massaging these spots enhances blood flow and improves soft tissue flexibility, which speeds up the recovery.
- Kinesiology Tape: In some cases, your therapist might suggest kinesiology taping to complement the effects of physiotherapy. This is a therapeutic bandage that helps reduce swelling, increase mobility and boost recovery in sprained muscles, joints, and ligaments.
- Shockwave therapy: This may be recommended for chronic (long term) pain that you have for more than six weeks.
- Elbow and Shoulder Stretches: Brachialis strain can cause certain nerves in your arm to become pinched. While this can aggravate the pain, the good news is that a few simple stretches and postural correction exercises can help you get rid of the symptoms effectively.
Most injuries to the brachialis muscle heal within 6 to 8 weeks. Depending on the nature and severity of your injury, your recovery might be a bit longer or even shorter. Do not delay seeking professional medical help, as it is the key to fast, proper and lasting recovery from a brachialis strain or tear.
Browse other articles by category
Physiotherapy for Knee Pain Physiotherapy For Slipped Disc Physiotherapy for Neck Pain PHYSIOTHERAPY
PHYSIOTHERAPY
 Hand Therapy
Hand Therapy
 Alternative
Alternative
 Massage
Massage
 Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment
Traditional Chinese Medicine Treatment
 Rehab
Rehab
 Physiotherapy For Lower Back Pain
Physiotherapy For Shoulder Pain
Orthopedic Doctors, Insurance & Healthcare
Physiotherapy For Upper Back Pain
Frozen Shoulder
Physiotherapy for Back Pain
Physiotherapy For Lower Back Pain
Physiotherapy For Shoulder Pain
Orthopedic Doctors, Insurance & Healthcare
Physiotherapy For Upper Back Pain
Frozen Shoulder
Physiotherapy for Back Pain
 Whatsapp us now
Whatsapp us now